本文简单介绍Binary indexed tree (Fenwick tree)
Fenwick tree
它又叫 Binary indexed tree ,也叫树状数组。
能在log(n)查询区间和,并且在log(n)时间内进行结点更新操作。
lowbit(x)函数
定义lowbit(x)为x的二进制表达式中最右边的1所对应的值。
比如,1234的二进制是0100 1101 0010 则 lowbit(1234)=2
在程序的实现中,Lowbit(x) = x & -x;(为什么这样写呢?因为计算机内部采用补码表示,-x是x按位取反,尾数+1的结果)
树的结构图
让我们来看看图:横坐标是x, 纵坐标是lowbit(x)
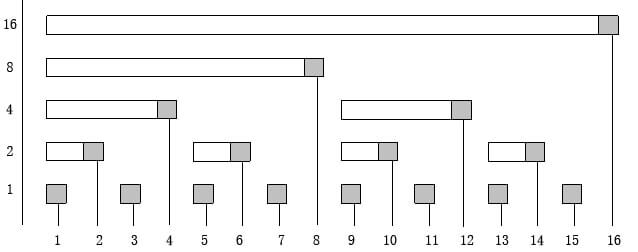 fenwick_tree_binary_index_tree
fenwick_tree_binary_index_tree
对于节点x:
- 为左子结点,则父结点的编号是
x + lowbit(x)
- 为右子结点,则父结点的编号是
x - lowbit(x)
设C[i] 为以i结尾的水平长条内的元素之和,如c[6]=a5+a6。
顺着结点i往左走,边走边往上爬,沿途经过的c[i]所对应的长条不重复不遗漏的包含了所有需要累加的元素。
如果修改了一个a[i] ,那么从c[i]往右走,边走边网上爬,沿途修改所有结点对应的c[i]即可。
- 如
a[1] + 1 那么c[1] + 1, c[2]+1,c[4]+1.........一直到最大值。
用C++ 的代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| inline int lowbit(int x) { return x & (-x); }
int sum(int x)
{
int ans = 0;
while(x > 0)
{
ans += C[x];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
return ans;
}
void add(int x,int d)
{
while(x <= N)
{
C[x] += d;
x += lowbit(x);
}
}
|
实现代码
写成类的话:
C++
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| class FenwickTree {
vector<int> sum_array;
int n;
inline int lowbit(int x) {
return x & -x;
}
public:
FenwickTree(int n) :n(n), sum_array(n + 1, 0) {}
void add(int x, int val) {
while (x <= n) {
sum_array[x] += val;
x += lowbit(x);
}
}
int sum(int x) {
int res = 0;
while (x > 0) {
res += sum_array[x];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
return res;
}
};
|
Python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| class FenwickTree(object):
def __init__(self, n):
self.sum_array = [0] * (n + 1)
self.n = n
def lowbit(self, x):
return x & -x
def add(self, x, val):
while x <= self.n:
self.sum_array[x] += val
x += self.lowbit(x)
def sum(self, x):
res = 0
while x > 0:
res += self.sum_array[x]
x -= self.lowbit(x)
return res
|


